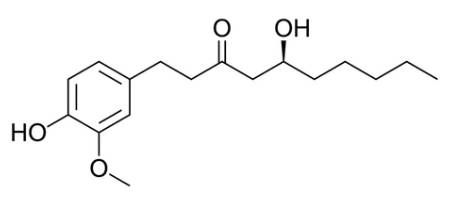
Ginger, scientifically known as Zingiber officinale, is the rhizome of a flowering plant belonging to the family Zingiberaceae, which also includes turmeric, cardamom, and galangal. Widely cherished as a spice, folk medicine, and culinary delicacy, ginger is notable for its rich array of bioactive compounds.
- Home
- About Us
-
Products
-
Featured Plants
- Panax Ginseng
- Panax Notoginseng
- Ginkgo Biloba
- Epimedium
- Morus Alba
- Glycine Max
- Sophora Flavescens
- Salvia Miltiorrhiza
- Rubia Cordifolia
- Pueraria Lobata
- Tripterygium Wilfordii
- Garcinia
- Atractylodes Lancea
- Glycyrrhiza Uralensis
- Scutellaria Baicalensis
- Curcuma Longa
- Zingiber Officinale
- Ganoderma Lucidum
- Cinnamomum Cassia
- Astragalus Membranaceus
- Lycium Chinense
- Atropa Belladonna
- Bupleurum Chinense
- Stevia Rebaudiana
- Vitis Vinifera
- Camellia Sinensis
- Angelica Dahurica
- Angelica Sinensis
- Uncaria Rhynchophylla
- Corydalis Yanhusuo
- Rosmarinus Officinalis
- Artemisia Annua
- Alisma Plantago-aquatica
- Siegesbeckia Orientalis
- Wolfiporia Cocos
- Gardenia Jasminoides
- Ophiopogon Japonicus
- Curcuma Zedoaria
- Psoralea Corylifolia
- Lonicera Japonica
- Polygala Tenuifolia
- Cimicifuga Foetida
- Hemsleya Amabilis
- Gelsemium Elegans
- Aconitum Carmichaelii
- Catharanthus Roseus
- Peucedanum Praeruptorum
- Schisandra Chinensis
-
Standard Extract
- Ginger Extract
- Ashwagandha Extract
- Senna Leaf Extract
- Wild Jujube Extract
- Garcinia Cambogia Extract
- Yucca Extract
- Saw Palmetto Extract
- Ginseng Extract
- Ginkgo Biloba Extract
- Rhodiola Rosea Extract
- Mulberry Leaf Extract
- Epimedium Extract
- Psyllium Husk Powder
- Gymnema Sylvestre Extract
- Rosemary Extract
- Curcuma Longa Extract
- Milk Thistle Extract
- Broccoli Extract
- Blueberry Extract
- Tribulus Terrestris Extract
- Wolfberry Extract
- Lotus Leaf Extract
- Hawthorn Berry Extract
- Semen Ziziphi Spinosae Extract
- Cassia Seed Extract
- Magnolia Bark Extract
- Cnidium Fruit Extract
- Soap Nut Extract
- Wood Butterfly Extract
- Green Coffee Bean Extract
- Vine Tea Extract
- Boswellia Extract
- Sophora Japonica Extract
- Cyanotis Arachnoidea Extract
- Cotinus Coggygria Extract
- Rice Bran Extract
- Olive Leaf Extract
- Shilajit Extract
-
Ratio Extract
- Okra Extract Powder
- Dandelion Extract
- Elderberry Extract
- Angelica Extract
- Cistanche Tubulosa Extract
- Cactus Extract
- Gotu Kola Extract
- Calendula Extract
- Alfalfa Extract Powder
- Thyme Extract
- Valerian Root Extract
- Kudzu Root Extract
- Sea Buckthorn Extract
- Purslane Extract
- Herba Houttuyniae Extract
- Parsley Extract
- Astragalus Extract
- Red Clover Extract
- Sunflower Seed Extract
- Gastrodia Elata Extract
- Safflower Extract
- Madder Extract
- Lotus Seed Extract
- Radix Isatidis Extract
- Tangerine Peel Extract
- Licorice Extract
- Artemisia Annua Extract
- St John's Wort Extract
- Active Monomer
-
Fruit & Vegetable Powder
- Kiwi Powder
- Acai Berry Powder
- Pitaya Powder
- Butterfly Pea Powder
- Banana Powder
- Pomegranate Extract Powder
- Strawberry Powder
- Pineapple Powder
- Cherry Powder
- Avocado Powder
- Cranberry Extract Powder
- Spinach Powder
- Carrot Powder
- Blood Orange Powder
- Watermelon Juice Powder
- Lemon Juice Powder
- Apple Juice Powder
- Grape Juice Powder
- Pear Juice Powder
- Tomato Extract Powder
- Organic Kale Powder
- Zucchini Powder
- Bilberry Extract Powder
- Lucuma Fruit Powder
- Black Sesame Seed Powder
- Ziziphus Jujuba Powder
- Artichoke Leaf Powder
- Dehydrated Cucumber Powder
- Soursop Fruit Powder
- Waxberry Juice Powder
- Pumpkin Powder
- Fig Fruit Powder
- Kumquat Powder
-
Mushroom Extract
- Reishi Mushroom Extract
- Chaga Mushroom Extract
- Maitake Mushroom Extract
- Cordyceps Extract
- Hericium Erinaceus Extract
- Shiitake Mushroom Extract
- Oyster Mushroom Extract
- Agrocybe Aegerita Extract
- Antrodia Camphorata Extract
- White Button Mushroom Extract
- Agaricus Blazei Extract
- Turkey Tail Mushroom Extract
- Poria Cocos Extract
- Tremella Fuciformis Extract
- Flammulina Velutipes Extract
- Black Fungus Extract
- Armillaria Mellea Extract
- Marasmius Androsaceus Extract
- Chanterelle Mushroom Extract
- Dictyophora Indusiata Extract
- Boletus Edulis Extract
- Polyporus Umbellatus Extract
- Phellinus Linteus Extract
- Coprinus Comatus Extract
- King Oyster Mushroom Extract
- Tiger Milk Mushroom Extract
- Sparassis Crispa Extract
- Hypsizygus Marmoreus Extract
- Morchella Esculenta Extract
- Fomes Fomentarius Extract
- Trametes Robiniophila Extract
- Tricholoma Matsutake Extract
-
Plant Peptide
- Walnut Peptide
- Corn Peptide
- Bitter Melon Peptide
- Mung Bean Peptide
- Soybean Peptide
- Pea Peptide
- Peanut Peptide
- Wheat Peptide
- Rice Peptide
- Spirulina Oligopeptide
- Mulberry Leaf Peptide Powder
- Hemp Seed Oligopeptide
- Highland Barley Peptide
- Jujube Peptide
- Maca Peptide
- Goji Berry Peptide
- Yam Peptide
- Sea Buckthorn Oligopeptide
- Astragalus Peptide
- Quinoa Peptide
-
Plant Pigment
- Sodium Copper Chlorophyllin
- Curcumin
- β-Carotene
- Lutein Powder
- Lycopene
- Roselle Powder
- Radish Red
- Gardenia Yellow
- Red Beet Powder
- Annatto Seed Powder
- Blue Spirulina Powder
- Alkannin
- Black Carrot Powder
- Capsicum Oleoresin
- Carthamin
- Lac Dye Red
- Monascus Red
- Perilla Red
- Red Cabbage Extract
- Gardenia Blue
- Gardenia Green
- Amaranthus Red
-
Natural Sweetener
- Stevia Extract
- Monk Fruit Extract
- Sweet Tea Extract
- Erythritol
- Allulose
- Stachyose
- Isomaltulose
- Trehalose
- D-Mannitol
- D-Tagatose
- L-Arabinose
- Inulin Powder
- Isomaltooligosaccharide Powder
- Fructooligosaccharide Powder
- Xylooligosaccharide Powder
- Rebaudioside D
- Rebaudioside A
- Rebaudioside M
- OEM & ODM Compound Sweetener
- Plant-Based Protein
-
Tea-Based Ingredients
- Instant Green Tea Extract
- Green Tea Extract EGCG (Epigallocatechin Gallate) 98%
- Instant Black Tea Extract
- Instant Pu-Erh Tea Extract
- Instant Oolong Tea Extract
- Instant White Tea Extract
- Matcha Powder
- Instant Hojicha Tea Powder
- Instant Jasmine Tea Extract
- Instant Chrysanthemum Extract
- Instant Rose Tea Powder
- Yerba Mate Extract
- Kombucha Powder
- Plant Polysaccharides
-
Plant-Derived Nanovesicles
- Ganoderma Lucidum-Derived Nanovesicles
- Curcuma Longa-Derived Nanovesicles
- Camellia Sinensis-Derived Nanovesicles
- Coix Lacryma-Jobi-Derived Nanovesicles
- Phalaenopsis Amabilis-Derived Nanovesicles
- Panax Ginseng-Derived Nanovesicles
- Aloe Vera-Derived Nanovesicles
- Dendrobium Officinale-Derived Nanovesicles
- Cocos Nucifera-Derived Nanovesicles
- Houttuynia Cordata-Derived Nanovesicles
- Citrus Limon-Derived Nanovesicles
- Plant Natural Products
-
Featured Plants
- Services
- Industries
- Quality System
- Resources
- Contact Us