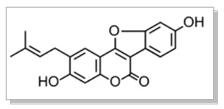
Psoralea corylifolia, commonly known as Babchi in Ayurvedic medicine and Bu Gu Zhi in Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), is a significant plant in the realm of herbal remedies. Belonging to the Fabaceae family, this plant is native to regions across India, China, and other parts of Asia. Renowned for its extensive medicinal properties, the seeds and other parts of Psoralea corylifolia have been utilized for thousands of years.
- Home
- About Us
-
Products
-
Featured Plants
- Panax Ginseng
- Panax Notoginseng
- Ginkgo Biloba
- Epimedium
- Morus Alba
- Glycine Max
- Sophora Flavescens
- Salvia Miltiorrhiza
- Rubia Cordifolia
- Pueraria Lobata
- Tripterygium Wilfordii
- Garcinia
- Atractylodes Lancea
- Glycyrrhiza Uralensis
- Scutellaria Baicalensis
- Curcuma Longa
- Zingiber Officinale
- Ganoderma Lucidum
- Cinnamomum Cassia
- Astragalus Membranaceus
- Lycium Chinense
- Atropa Belladonna
- Bupleurum Chinense
- Stevia Rebaudiana
- Vitis Vinifera
- Camellia Sinensis
- Angelica Dahurica
- Angelica Sinensis
- Uncaria Rhynchophylla
- Corydalis Yanhusuo
- Rosmarinus Officinalis
- Artemisia Annua
- Alisma Plantago-aquatica
- Siegesbeckia Orientalis
- Wolfiporia Cocos
- Gardenia Jasminoides
- Ophiopogon Japonicus
- Curcuma Zedoaria
- Psoralea Corylifolia
- Lonicera Japonica
- Polygala Tenuifolia
- Cimicifuga Foetida
- Hemsleya Amabilis
- Gelsemium Elegans
- Aconitum Carmichaelii
- Catharanthus Roseus
- Peucedanum Praeruptorum
- Schisandra Chinensis
-
Standard Extract
- Ginger Extract
- Ashwagandha Extract
- Senna Leaf Extract
- Wild Jujube Extract
- Garcinia Cambogia Extract
- Yucca Extract
- Saw Palmetto Extract
- Ginseng Extract
- Ginkgo Biloba Extract
- Rhodiola Rosea Extract
- Mulberry Leaf Extract
- Epimedium Extract
- Psyllium Husk Powder
- Gymnema Sylvestre Extract
- Rosemary Extract
- Curcuma Longa Extract
- Milk Thistle Extract
- Broccoli Extract
- Blueberry Extract
- Tribulus Terrestris Extract
- Wolfberry Extract
- Lotus Leaf Extract
- Hawthorn Berry Extract
- Semen Ziziphi Spinosae Extract
- Cassia Seed Extract
- Magnolia Bark Extract
- Cnidium Fruit Extract
- Soap Nut Extract
- Wood Butterfly Extract
- Green Coffee Bean Extract
- Vine Tea Extract
- Boswellia Extract
- Sophora Japonica Extract
- Cyanotis Arachnoidea Extract
- Cotinus Coggygria Extract
- Rice Bran Extract
- Olive Leaf Extract
- Shilajit Extract
-
Ratio Extract
- Okra Extract Powder
- Dandelion Extract
- Elderberry Extract
- Angelica Extract
- Cistanche Tubulosa Extract
- Cactus Extract
- Gotu Kola Extract
- Calendula Extract
- Alfalfa Extract Powder
- Thyme Extract
- Valerian Root Extract
- Kudzu Root Extract
- Sea Buckthorn Extract
- Purslane Extract
- Herba Houttuyniae Extract
- Parsley Extract
- Astragalus Extract
- Red Clover Extract
- Sunflower Seed Extract
- Gastrodia Elata Extract
- Safflower Extract
- Madder Extract
- Lotus Seed Extract
- Radix Isatidis Extract
- Tangerine Peel Extract
- Licorice Extract
- Artemisia Annua Extract
- St John's Wort Extract
- Active Monomer
-
Fruit & Vegetable Powder
- Kiwi Powder
- Acai Berry Powder
- Pitaya Powder
- Butterfly Pea Powder
- Banana Powder
- Pomegranate Extract Powder
- Strawberry Powder
- Pineapple Powder
- Cherry Powder
- Avocado Powder
- Cranberry Extract Powder
- Spinach Powder
- Carrot Powder
- Blood Orange Powder
- Watermelon Juice Powder
- Lemon Juice Powder
- Apple Juice Powder
- Grape Juice Powder
- Pear Juice Powder
- Tomato Extract Powder
- Organic Kale Powder
- Zucchini Powder
- Bilberry Extract Powder
- Lucuma Fruit Powder
- Black Sesame Seed Powder
- Ziziphus Jujuba Powder
- Artichoke Leaf Powder
- Dehydrated Cucumber Powder
- Soursop Fruit Powder
- Waxberry Juice Powder
- Pumpkin Powder
- Fig Fruit Powder
- Kumquat Powder
-
Mushroom Extract
- Reishi Mushroom Extract
- Chaga Mushroom Extract
- Maitake Mushroom Extract
- Cordyceps Extract
- Hericium Erinaceus Extract
- Shiitake Mushroom Extract
- Oyster Mushroom Extract
- Agrocybe Aegerita Extract
- Antrodia Camphorata Extract
- White Button Mushroom Extract
- Agaricus Blazei Extract
- Turkey Tail Mushroom Extract
- Poria Cocos Extract
- Tremella Fuciformis Extract
- Flammulina Velutipes Extract
- Black Fungus Extract
- Armillaria Mellea Extract
- Marasmius Androsaceus Extract
- Chanterelle Mushroom Extract
- Dictyophora Indusiata Extract
- Boletus Edulis Extract
- Polyporus Umbellatus Extract
- Phellinus Linteus Extract
- Coprinus Comatus Extract
- King Oyster Mushroom Extract
- Tiger Milk Mushroom Extract
- Sparassis Crispa Extract
- Hypsizygus Marmoreus Extract
- Morchella Esculenta Extract
- Fomes Fomentarius Extract
- Trametes Robiniophila Extract
- Tricholoma Matsutake Extract
-
Plant Peptide
- Walnut Peptide
- Corn Peptide
- Bitter Melon Peptide
- Mung Bean Peptide
- Soybean Peptide
- Pea Peptide
- Peanut Peptide
- Wheat Peptide
- Rice Peptide
- Spirulina Oligopeptide
- Mulberry Leaf Peptide Powder
- Hemp Seed Oligopeptide
- Highland Barley Peptide
- Jujube Peptide
- Maca Peptide
- Goji Berry Peptide
- Yam Peptide
- Sea Buckthorn Oligopeptide
- Astragalus Peptide
- Quinoa Peptide
-
Plant Pigment
- Sodium Copper Chlorophyllin
- Curcumin
- β-Carotene
- Lutein Powder
- Lycopene
- Roselle Powder
- Radish Red
- Gardenia Yellow
- Red Beet Powder
- Annatto Seed Powder
- Blue Spirulina Powder
- Alkannin
- Black Carrot Powder
- Capsicum Oleoresin
- Carthamin
- Lac Dye Red
- Monascus Red
- Perilla Red
- Red Cabbage Extract
- Gardenia Blue
- Gardenia Green
- Amaranthus Red
-
Natural Sweetener
- Stevia Extract
- Monk Fruit Extract
- Sweet Tea Extract
- Erythritol
- Allulose
- Stachyose
- Isomaltulose
- Trehalose
- D-Mannitol
- D-Tagatose
- L-Arabinose
- Inulin Powder
- Isomaltooligosaccharide Powder
- Fructooligosaccharide Powder
- Xylooligosaccharide Powder
- Rebaudioside D
- Rebaudioside A
- Rebaudioside M
- OEM & ODM Compound Sweetener
- Plant-Based Protein
-
Tea-Based Ingredients
- Instant Green Tea Extract
- Green Tea Extract EGCG (Epigallocatechin Gallate) 98%
- Instant Black Tea Extract
- Instant Pu-Erh Tea Extract
- Instant Oolong Tea Extract
- Instant White Tea Extract
- Matcha Powder
- Instant Hojicha Tea Powder
- Instant Jasmine Tea Extract
- Instant Chrysanthemum Extract
- Instant Rose Tea Powder
- Yerba Mate Extract
- Kombucha Powder
- Plant Polysaccharides
-
Plant-Derived Nanovesicles
- Ganoderma Lucidum-Derived Nanovesicles
- Curcuma Longa-Derived Nanovesicles
- Camellia Sinensis-Derived Nanovesicles
- Coix Lacryma-Jobi-Derived Nanovesicles
- Phalaenopsis Amabilis-Derived Nanovesicles
- Panax Ginseng-Derived Nanovesicles
- Aloe Vera-Derived Nanovesicles
- Dendrobium Officinale-Derived Nanovesicles
- Cocos Nucifera-Derived Nanovesicles
- Houttuynia Cordata-Derived Nanovesicles
- Citrus Limon-Derived Nanovesicles
- Plant Natural Products
-
Featured Plants
- Services
- Industries
- Quality System
- Resources
- Contact Us