- Home
-
Industries
-
Environment Testing
- Construction Dust Testing
- Drinking Water Testing
- Emerging Contaminants Testing
- Sea Water Testing
- Sludge Testing
- Soil Testing
- Solid Waste
- Stack Emissions Testing
- Stormwater Testing
- Subsurface Vapour Intrusion Assessment
- Surface Water Testing
- Wastewater Testing
- Watersheds and Rivers Testing
- Well Water Testing
- Asbestos Testing
- Mold Testing
-
Food Testing
- Beverage Testing
- Biscuit Testing
- Candy Testing
- Canned Food Testing
- Coffee Testing
- Condiments Testing
- Cooking Oil Testing
- Fast Food and Snack Testing
- Infant Food Testing
- Liquor Testing
- Meat and Meat Product Testing
- Milk & Dairy Testing
- Pet Food Testing
- Refrigerated and Frozen Food Testing
- Seafood Testing
- Tomato Products Testing
- Agricultural Products & Crops Testing
- Material Testing
- Chemical Products Testing
- Petroleum Products Testing
- Personal Care & Beauty Products Testing
- Household and Apparel Products Testing
- Healthcare Products Testing
- Building Products Testing
- Stationery and Office Supplies Testing
- Safety Testing of Nano Products
- Children Products Testing
-
Environment Testing
-
Services
- Agriculture & Crop Analytical Services
- Energy Analytical Services
- Environmental Analytical Services
- Food Analytical Services
- Material Characterization Services
-
Pharmaceutical Analytical Services
- Biopharmaceutical Characterization Services
- Deformulation (Reverse Engineering) Analysis Services
- Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Failure Analysis Services
- Pharmaceutical Impurity Testing Services
- Pharmaceutical Separation and Purification Services
- Preformulation Analysis Services
- Stability Analysis Services
- Compendial Testing
- Dissolution Testing
- Water Content Determination
- Pharmaceutical Water Testing
- Potency Testing
- Pharmaceutical Microbiology Testing
- Retail Products Analytical Services
- Textile Testing Services
- Karl Fischer (KF) Moisture Testing
-
Recommended Services
- Failure Analysis and Investigations
- Food Testing
- Pharmaceutical Testing
- Surfactant Testing
- Cosmetics and Skin Care Products Testing
- Karl Fischer (KF) Moisture Testing Service
- Textile Testing
- Microplastic Analysis and Testing
- Mold Testing Service
- Lubricating Oil Analysis and Testing
- Alloy Material Testing
- Deformulation Service
- Semiconductor Testing Services
- Techniques
- AI SmartQC Platform
-
Resources
- Regulatory Resources
- Blog
- Application Notes
- Video Library
- White Paper
- Flyer
- Case Study
- Fee Schedule
-
Protocol
- Protocol for Deformulation of Pharmaceutical Products
- Experimental Procedure for Determining Trace Moisture in Food by Karl Fischer Method
- Experimental Procedure for Determining Moisture Content in Interior Wall Paint Using Karl Fischer Method
- Testing of Color Fastness to Rubbing for Textiles
- Qualitative Identification of Textile Fibers by Five Experimental Methods
- Tablet Dissolution Test - Determination of Dissolution Rate and Dissolution Rate of Azithromycin Dispersible Tablets
- Determination of Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) in Water - Potassium Dichromate Method
- How to Detect Bacteria in Food: Total Bacterial Count Procedure
- Testing Coliforms in Food: MPN & Plate Count Methods
- Determination of Aflatoxin B1 in Food: ELISA & TLC Methods for Accurate Detection
- Determination of Molds and Yeasts in Food: Plate Count Methods for Accurate Detection
- Determination of Lubricating Oil Liquid Density - Density Meter Method
- Determination of Acid Value in Lubricating Oil - Potentiometric Titration Method
- ELISA Experimental Procedure for Detecting Aflatoxin B1 in Peanuts
- Experimental Guide: Standard Procedures for Semiconductor Device DC Parametric Testing
- Careers
- About
- Contact
- Home
- Resources
- Regulatory Resources
- Foods
- Content and Concentration of Caffeine in Coffee
Content and Concentration of Caffeine in Coffee
InquiryThrough our global network of testing experts and analytical equipment including chromatography (HPLC, GC, GC/MS) and atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS, GFA, FIAS), Our goal is to provide test services as efficiently as possible to maximize our customers' profits. For more information about our services, contact one of our experts today.
Note: this service is for Research Use Only and Not intended for clinical use.
Coffee
Coffee is a drink made from roasted coffee beans. The main ingredients of coffee are caffeine, tannin, fat, acid fat, volatile fat, protein, sugar, fiber, minerals and so on. Drinking coffee is a double-edged sword. On the one hand, it promotes skin metabolism, activates the digestive organs, and has a hangover function. On the other hand, it aggravates high blood pressure and induces osteoporosis and affects sleep.
Caffeine
Caffeine is a xanthine alkaloid compound. Pure caffeine is white, intensely bitter powder. Its chemical formula is C8H10N4O2, chemical name is 1,3,7-trimethylxanthine or 3,7-dihydro-1,3,7-trimethyl-1H-indole-2,6-dione, molecular weight is 194.19.
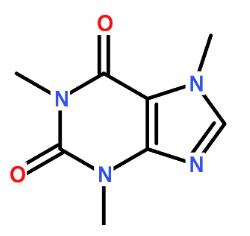
Figure1. Chemical structure of caffeine
The Efficacy and Harm of Caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system stimulant that has an extensive stimulating effect on central nervous system. It can stimulate the cerebral cortex, increase the excitatory process of the cerebral cortex, restore mental vitality, reduce fatigue, eliminate drowsiness, and improve mental activity. In addition, it plays an active role in cardiovascular system, promoting acid secretion in stomach and treating diseases such as migraines. When the dose is increased or the vital center of the ventricle is suppressed, it can directly stimulate the respiratory center and the vascular movement center, thereby deepening breath and increasing blood pressure. There is also a weak excitatory heart and diuretic effect. However, excessive caffeine can be harmful. Excessive caffeine, usually more than 250 mg (equivalent to 2-3 cups of brewed coffee), can cause central nervous system overstrain. Symptoms of overexcited caffeine include restlessness, nervousness, excitement, sleeplessness, blushing, increased urine production, gastrointestinal dysfunction, muscle twitching, distraction, irregular or rapid heartbeat, and restlessness. High doses of caffeine can lead to death. In experimental rats, half of the lethal dose of caffeine was 192 mg/kg body weight. But the amount of caffeine in general that produces different effects depends on weight and personal sensitivity, which is about 150 to 200 mg per kilogram of body weight. About 140 to 180 cups of coffee are consumed by the average adult for a limited period of time, potentially leading to death. Although it's almost impossible to kill people by drinking regular coffee, there have been reports of deaths from overconsumption of coffee.
The Amount of Caffeine in Coffee
The federal regulations governing the use of caffeine also establish a “tolerance” for manufacturers, who wish to add caffeine to their products. In fact, 21 Code of Federal Regulations section182.1180 (b) states that caffeine's tolerance is 0.02%. This means that any product manufactured with caffeine must have 0.02% or less will be considered safe. For example, a 12 oz drink can have 68 mg of caffeine and still meet the 0.02% limit. Different types of coffee have different amounts of caffeine. According to the U.S. department of agriculture, the average instant coffee has about 57 mg/1.8 g caffeine, the picture below shows the content of each ingredient in the best-selling coffee.

Figure 2. The content of each ingredient in the best-selling coffee
Factors Affecting Caffeine Content and Concentration
While caffeine itself is a bit bitter, the taste of coffee is essentially independent of how much caffeine it contains. Therefore, the concentration and content of caffeine cannot be judged by the taste of coffee. Its concentration is mainly related to the mixing of coffee beans, extraction, grinding, roasting stage and water temperature.
Recommended Daily Intake of Caffeine
Studies have shown that daily coffee intake of no more than 6 mg/kg will not have a negative impact on the human body. The daily intake should not be more than 360 mg for 60 kg person. If each cup of coffee is 236 mL (1.8 g instant coffee powder/serving), the caffeine content is 57 mg, then the maximum limit of instant coffee for one day is 6 cups. If you have caffeine from other sources: such as functional drinks, tea, and chocolate, then you should have fewer cups of coffee. Although coffee has a refreshing effect, you can not dependent on drinking a lot of coffee for a long time, which will cause harm to the body and have certain dependence. At the same time, everyone's sensitivity and tolerance to caffeine are different, so the specific situation varies from person to person.
Related Regulations
2. FDA Regulations for Caffeine

Alfa Chemistry is a professional analytical testing company, and has long been committed to promoting the long-term development of the analytical testing industry, delivers innovative and bespoke assurance, testing and inspection solutions for our customers’ operations and supply chains. We sincerely welcome colleagues from all walks of life to come to negotiate and cooperate.
Related Services
- Recommendation
- Ordering Process
- Ask a Question
Do not know how to place an order, please refer to the flow chart shown below.
Submit quotation request |
A technical manager will contact you within 24 hours |
You will review and approve the final price and place an order |
Confirm with you and make the payment |
Instruct you to ship your samples and form |
Analytic report delivery |

